Most people are of the opinion that scarlet fever, chicken pox and other childhood diseases are part of a child’s growth; in most cases some childhood diseases cannot be avoided.
By going through them, children will develop immunity, which is durable. For some childhood diseases there are already mandatory vaccines available, such as the Measles and Rubella.
Chickenpox is a childhood disease that continues to be a reason for periodic epidemics in kindergartens and schools. The body of the child builds lasting immunity and there are very rare cases of Chickenpox recurrence.
What is Scarlatina and why we should keep our children safe from it?
Scarlet fever (Scarlatina) is very unpleasant infectious disease that manifests with a characteristic rash and therefore it is compared to other childhood diseases – Chickenpox and Rubella. Scarlatina is a disease in which the body of the small child cannot build itself immunity and they could get sick several times. Moreover, it is a quite serious illness. Chickenpox does not need treatment but scarlet fever requires treatment with antibiotics.
What kind of disease is scarlet fever?
Scarlet fever is a streptococcal infection, which is caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus group A. Infection with this streptococcus, which is very resistant to external environment and produces toxins and enzymes, can cause serious damage to the body of the child.
In many cases there is a likelihood of infestation, which means that a seemingly healthy child can transmit the disease because the child is a carrier of the strep, but does not show any symptoms.
The streptococci are inside the mucus of the nose and throat and are transmitted by droplets and direct contact with a sick child or a carrier of streptococcus. Transmission of streptococcus through objects for example toys is also possible. It is very rarely passed on through milk. As a source of infection can be children with atypical form of the disease – analogue streptococcal angina. Receptivity is stronger in children aged 1 to 10 years old. New born babies and infants up to 6 months of age are not affected by Scarlet Fever.
The streptococci enter the body of the child after they have fallen already in the lining of the throat. In very rare cases where the child has a skin disorder, streptococci can enter through the skin. In place of penetration causative – strep formed inflammatory changes with pus and necrosis. Toxins enter the blood and cause general inflammation of the body and a specific effect on the skin, resulting in a characteristic rash impact on the nervous system, the cardiovascular system and the kidneys.
After the second week of the disease, (if it is not treated with antibiotics) allergic process start to develop and the occurrence of allergic inflammatory changes in the myocardium, joints and kidneys.
During the period of illness specific immune bodies are formed, their production is reduced by the applied antibiotics in the treatment, and this leads to an insufficient immune system.
In practice, if not treated with antibiotics streptococcus causes serious damage to vital organs in the body of the child. Treatment with antibiotics does not allow the establishment of immunity.
How to recognize scarlet fever?
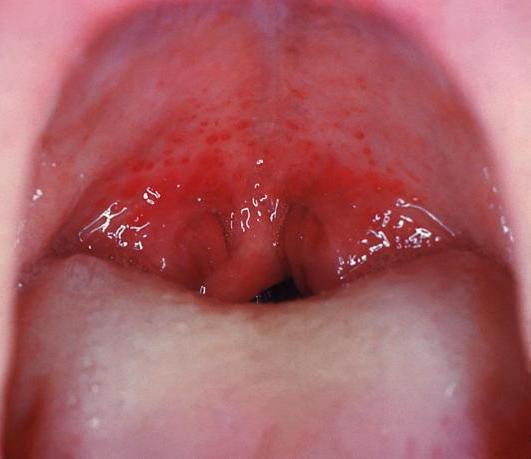
The incubation period of scarlet fever is usually lasts around 10 days. Typically, the first symptoms will appear between the 4th and 8th day after the inoculation of the child. The child will have a fever and sore throat and this is often accompanied by vomiting. The child may also have a severe sore throat, no appetite and complaints of a headache. A review has established typical angina with swollen and reddened mucous membrane of the throat, which is strongly distinguished from the normal mucosa of the soft palate. In many cases there are whitish grey spots on the tonsils. Small reddish spots may also appear in the lining of the soft palate. The child’s tongue may be heavily taxed; regional lymph nodes could be enlarged and very painful.
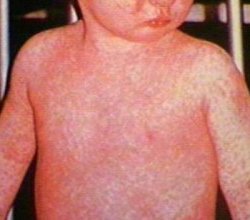
A rash on the skin will appear in the first 12-24 hours but rarely on the second day. It may the torso (better expressed in the inguinal folds) and limbs. The child’s face will appear quite red and a triangle of pale skin without a rash could appear around the lips and nose – ie. Triangle of Filatov. Rashes are very typical –pink buds that make the skin look red. The skin may feel rough to touch and it could be mildly itchy for the child. Red stripes appear in articular folds resulting from the merger of pimples – symptom Paste.
When children are ill due to scarlet fever, they are in a poor general condition. The liver in many cases is slightly increased with affected functions. The fever can remain high for three to four days, and falls critically or gradually. On the fifth day the angina is already passed. From the second day the tongue begins to change, the taste buds swell and turn red this is known as “Raspberry tongue”.

The rash will gradually start to fade and after 8-9 days it should disappear completely, but is accompanied by a characteristic skin peeling. The urine shows the presence of protein, acetone, increased urobilinogen. In the blood count it will show leukocytosis, polinukleoza, moderate eosinophilia and accelerated Rouet. Microbiological testing in secretions from the throat isolated beta-hemolytic streptococci.
In some cases, scarlet fever can occur in a much milder form with a very mild rash, sometimes only in the inguinal folds. Angina and raspberry tongue however, are always present. Scarlet fever without a rash is also possible – i.e. analog angina.
Scarlatina complications
Early complications – toxic action of streptococcus causes otitis, purulent lymphadenitis, necrotic angina and others.
Late complications – usually after the second week they are primarily attributable to allergenic effects. These include acute scarlet glomerulonephritis, which appears to 20 days with swelling, pallor, changes in the urine and elevated blood pressure and damage to the cardiovascular system. The damage to the cardiovascular system can occur in the first week of the illness with so-called heart including abnormal rhythm and muted tones, extrasystolic arrhythmia. The prognosis of this complication is favourable, but later complication can occur scarlet myocarditis, which is very serious.
In some cases, though rarely, scarlet fever can cause damage to the joints and rheumatic diseases.
All these possible complications caused by scarlet fever have shown that it is not at all a harmless childhood disease and it is very important to be treated on time and prophylaxis in children’s collectives in order to minimize the disease.
Measures for prevention and treatment of scarlet fever
If there is any suspicion that the child may develop the disease, they should be taken for throat swabs for early diagnosis and to identify the presence of beta streptococci in the throat. Timely microbiological testing enables the preparation of anitbiogram and determination of the treatment with the appropriate antibiotic, this is extremely important. In kindergarden all children who are in contact with a sick child should be examined microbiologically by taking throat swabs and if there is presence of strep to undergo antibiotic treatment to prevent the development of scarlet fever, subsequent complications and the spread of the disease. After treatment it is necessary to examine control throat swabs and children who have suffered from scarlet fever to be under observation for at least one month by making preventive tests of blood, urine and consultation with a cardiologist.
Prevention is crucial and early detection of the disease always prevents complications that can be very serious. It is therefore important to know scarlet fever well as a disease and to look at it as a serious illness. It is a question of health culture!
 Happy at Home Family Problems & Solutions | Home & Health Tips
Happy at Home Family Problems & Solutions | Home & Health Tips
